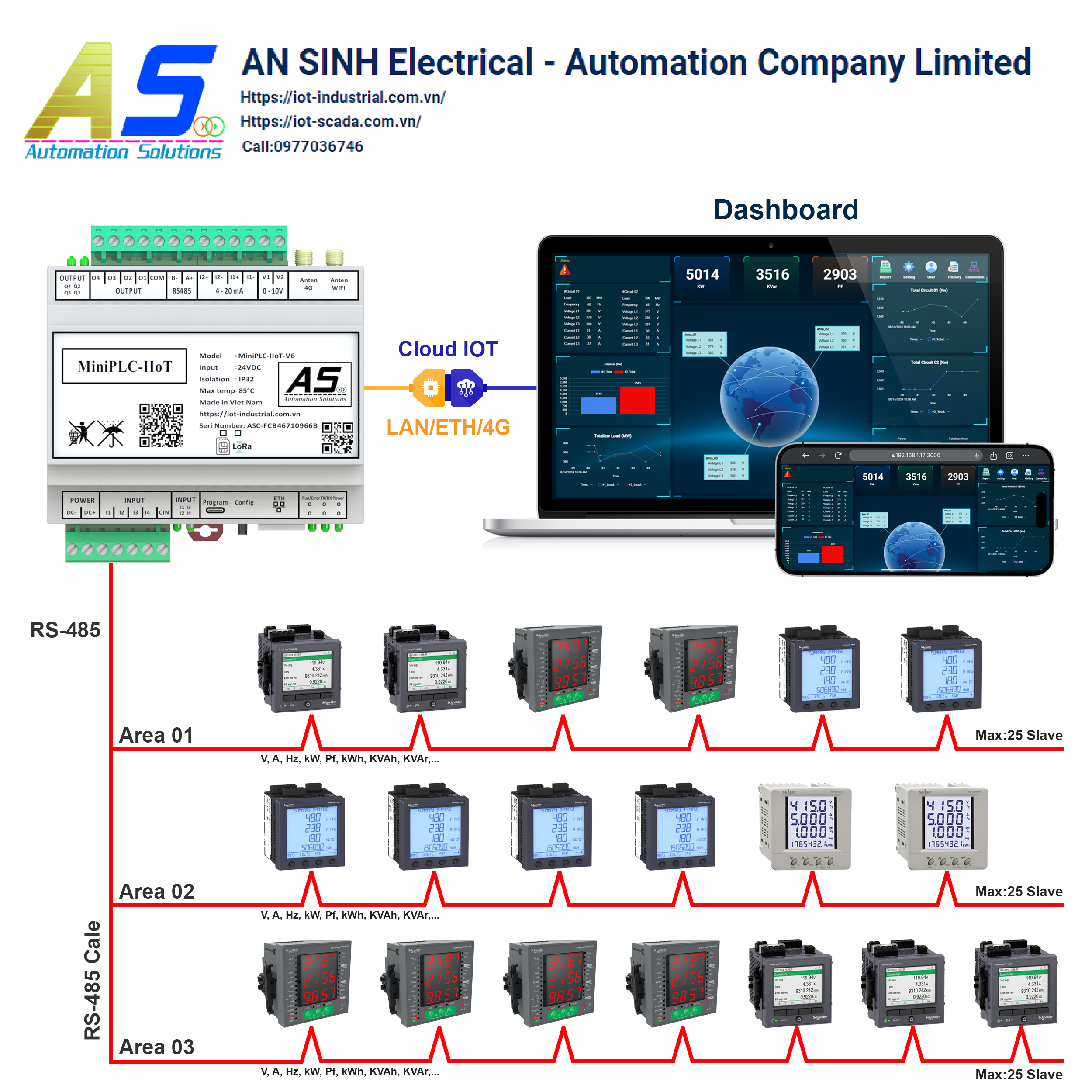
1. Role of MiniPLC in the power monitoring system:
- Data collection: MiniPLC acts as a control center, connecting to power measurement sensors such as electronic meters, current sensors, and voltage sensors. From there, it collects real-time power consumption data, providing continuous information about the operation of the power system.
- Data processing: After collection, MiniPLC processes this data to calculate parameters such as total electricity consumption, average consumption, and instantaneous capacity. It also compares these parameters with preset values to detect abnormalities or suboptimal performance.
- Device control: Based on processed data, MiniPLC can automatically control electrical devices. For example, it can turn off unnecessary devices when not in use or adjust device power to optimize energy.
- Data transmission: After processing, data will be transmitted to the central server or IoT platform. Here, data will be stored, analyzed, and displayed via dashboard, helping users have an overview of the system.
2. Benefits of using MiniPLC:
- Detailed monitoring: MiniPLC allows detailed monitoring of each device and power consumption area, helping to identify large energy consumption points and provide effective saving measures.
- Early warning: The system has the ability to automatically detect and report electrical problems, such as overload or abnormal energy consumption, helping users react promptly.
- Energy optimization: By adjusting and controlling power consumption, the system helps reduce costs and increase energy efficiency.
- Simplify management: All relevant data is centralized and displayed on a single interface, helping users easily monitor and manage the system intuitively and effectively.
- Flexible: MiniPLC has the ability to be easily configured and flexibly expanded to suit many different types of systems and scales.
3. Main components of the system:
- MiniPLC: Is the control center of the system, performing the functions of collecting, processing and controlling the device.
- Power meter: This device measures parameters such as current, voltage and power.
- Control equipment: Includes relays and contactors used to turn on/off electrical equipment when needed.
- Communication network: Connect all devices in the system to each other and to the central server to ensure continuous and timely information.
- Central server: This is the place to store, analyze data, and create reports necessary for monitoring and management.
- Dashboard: Intuitive interface displays important data and parameters of the system, helping users easily monitor and control.
4. Operational process:
- Data collection: MiniPLC continuously collects data from power meters and sensors.
- Data processing: Data is processed and compared with preset values.
- Control: If there is a problem or adjustment is needed, MiniPLC will send control signals to the devices.
- Data transmission: Data is transmitted to the central server.
- Display: Data is displayed on the dashboard for users to monitor.
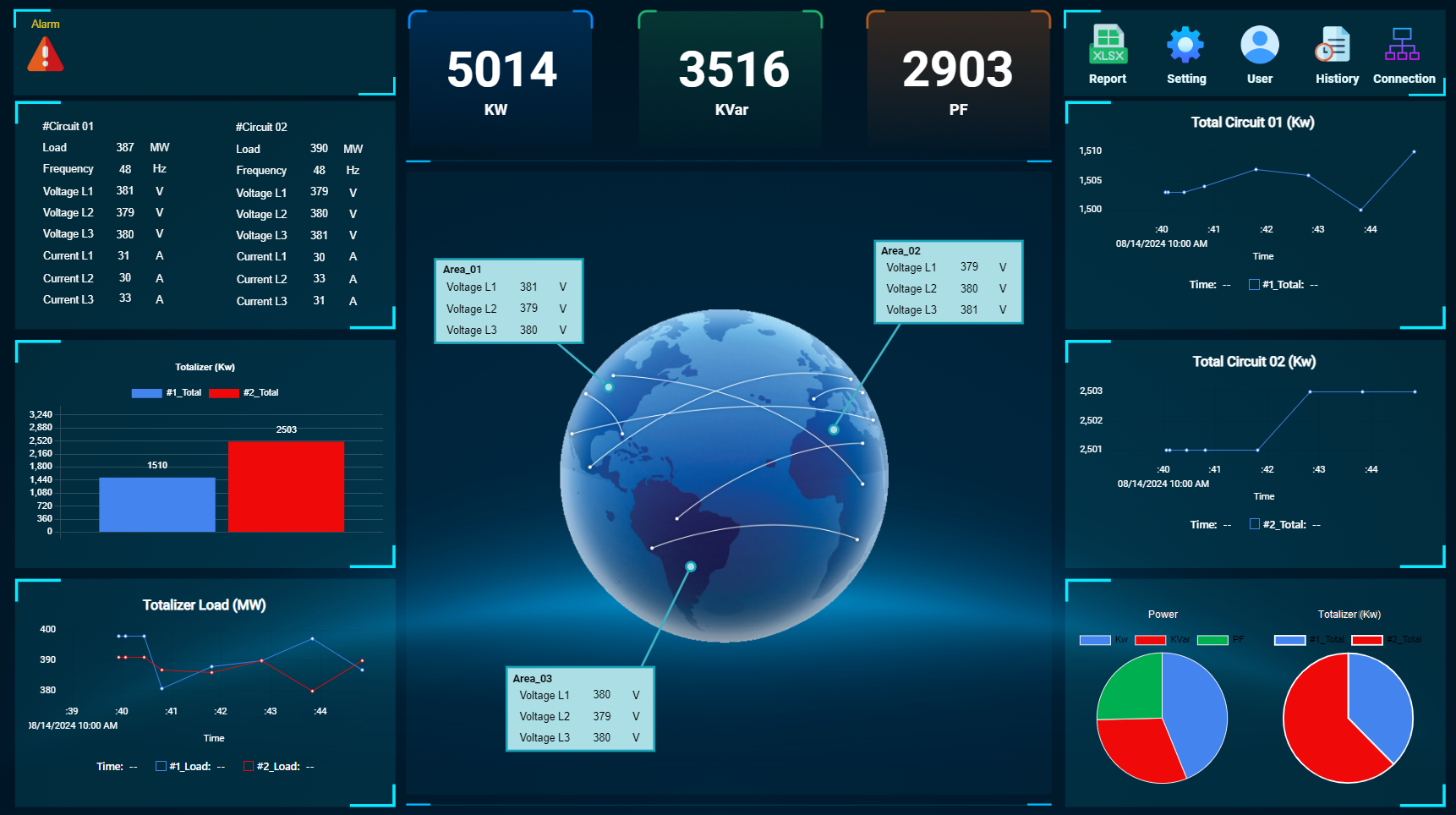
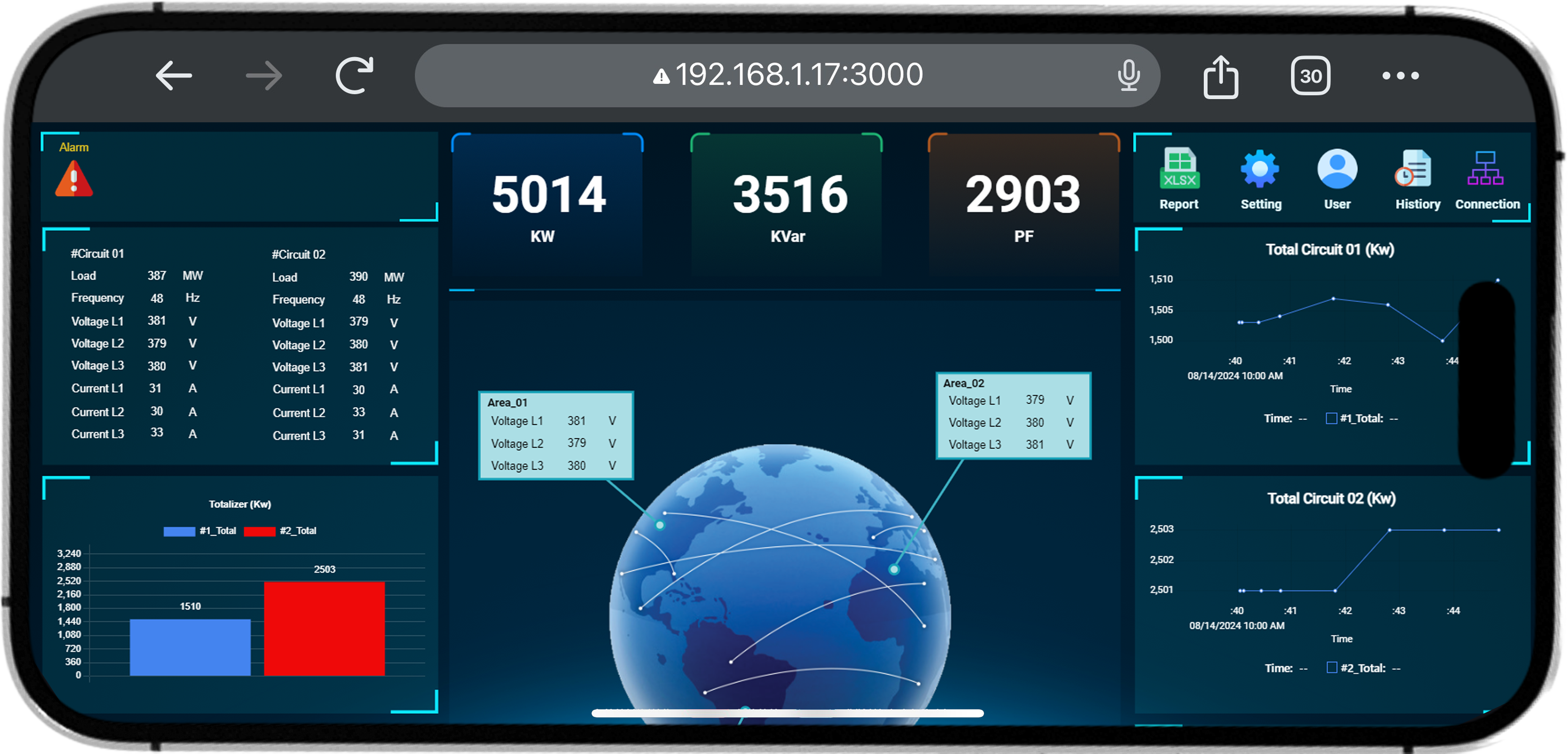
5. Dashboard features:
- Graph display: Allows users to view changes in power consumption over time through visual graphs.
- Report: The system generates detailed reports on power consumption over cycles such as day, week, month, and year, helping users evaluate energy use efficiency.
- Warning: When there is a problem or power consumption exceeds the allowed limit, the system will send a warning message to the user so that they can intervene promptly.
- Remote control: Users can control devices remotely through the dashboard interface, making system management more convenient.
6. Equipment management and maintenance:
- Monitor equipment status: Monitor the operating status of equipment to detect problems early and schedule maintenance.
- Automatic maintenance schedule: Supports periodic maintenance planning for devices to maintain performance and extend lifespan.
7. Security and access
- User management: The system needs to provide a decentralization mechanism, ensuring that only authorized people can access important functions.
- Data security: Ensure data security through encryption, protecting data from unauthorized access and other cybersecurity risks.
8. Scalability
- System expansion: The system needs to be flexible and easy to expand when the business increases in scale or when it needs to integrate new devices and sensors.
- Easy upgrades: The system needs to support software updates and upgrades without affecting the continued operation of the system.